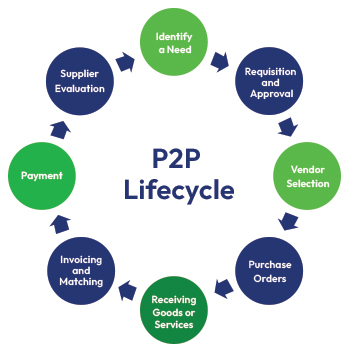
Procure to Pay (P2P) also referred to as Purchase to Pay, is essential to managing an organization’s procurement and financial process. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of acquiring goods and services beginning with vendor selection and requisition requests to procurement and invoice payments. Procure to Pay is a complex process that requires integrating functions across procurement, finance, accounts, and payable systems.
Given the expansive nature of the Procure to Pay process, it is often difficult to identify fraudulent activities which can be committed by internal (employees), external (third-party vendors), or involving both parties. Procure to Pay (P2P) fraud tends to occur across three broad focus areas: Invoices, Payments, and Purchase Orders resulting in significant financial loss for the organization.